

Navigating tipping laws and their implications is essential for businesses in Ireland. Tipping plays a vital role in supplementing employee income, impacting turnover rates and operational costs. Moreover, compliance with legal regulations ensures businesses avoid fines and fosters transparency, motivating staff to enhance customer service. Now, let’s delve into the key aspects of tipping laws in Ireland and their impact on business operations.

Since the introduction of the Payment of Wages (Amendment) (Tips and Gratuities) Act 2022 there are clear guidelines on the treatment of tips between businesses and employees.
In Summary:
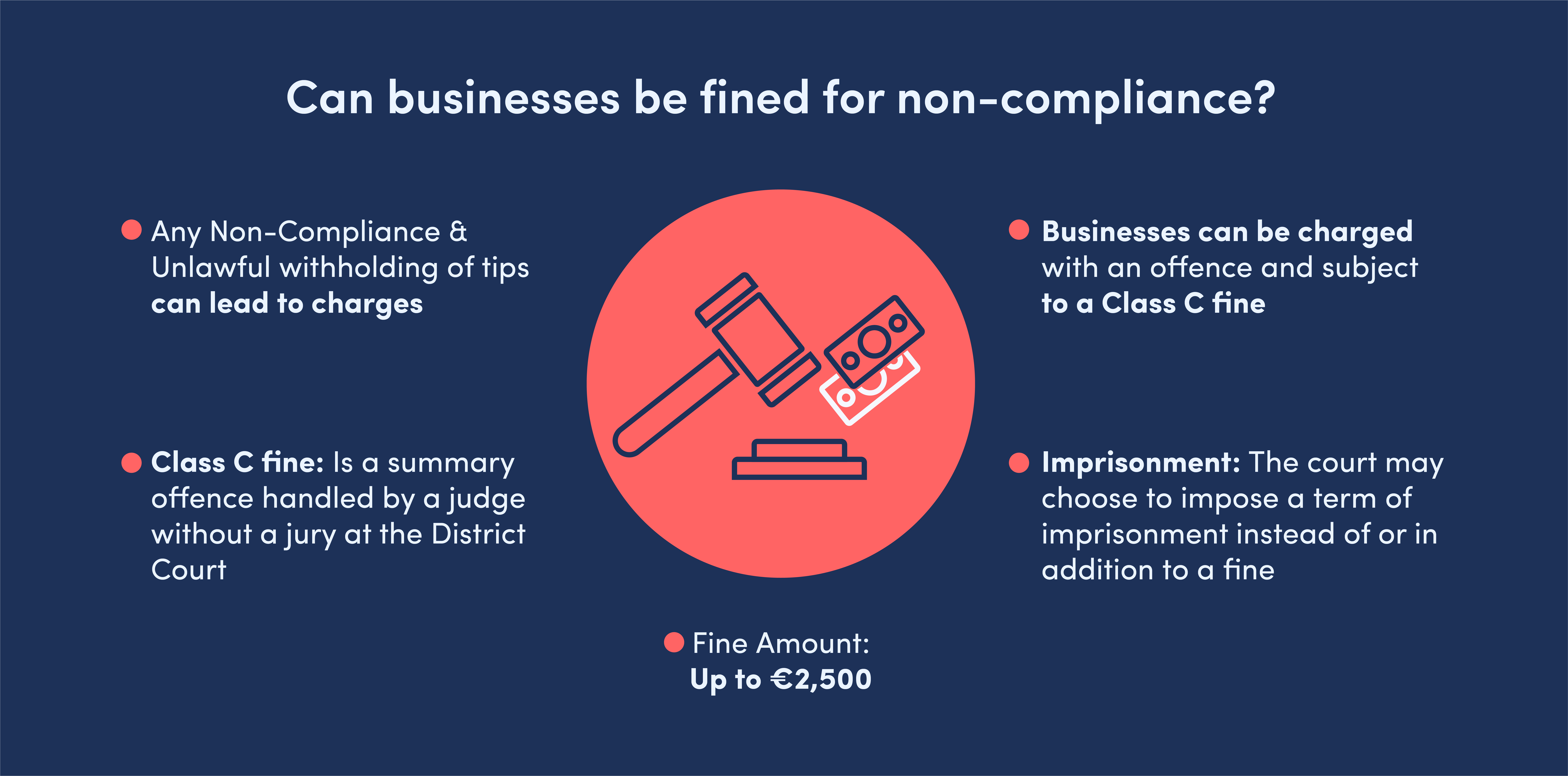
If businesses do not follow the legislation then they are committing an offence and liable to a Class C fine.
Based on the regulations there are multiple factors businesses need to consider and make sure they are compliant with. This includes how they organise their business operations, organisation of transactions, tax compliance and potential impacts on staff turnover.
In Ireland, tipping law affects how businesses handle their finances and interact with employees. The legislation requires thorough financial planning and affects how service charges and cash tips are distributed through payroll.
Businesses must adapt their payroll systems to accommodate tips, which are not considered part of an employee’s contractual pay but instead a gratuity provided directly by the customer.
Employers need to ensure they accurately record all received tips due to their tax implications.Tips given through electronic methods, like cards, are usually tracked and managed via payroll. This demands careful accounting to maintain transparency and adhere to tax regulations.
Businesses need to determine how tips are distributed between themselves and their employees. A Tronc system can help provide a fair solution of how tips are distributed between all parties.

Employers in Ireland must strictly follow the tipping laws to guarantee fair labour practices and prevent legal consequences.
It is crucial that businesses understand the Payment of Wages (Amendment) (Tips and Gratuities) Act 2022 in full so they do not risk being fined.
If an owner unlawfully withholds tips intended for employees, they could be charged with an offence and may receive a class C fine on summary conviction.
A summary offence is a legal matter resolved by a judge at the District Court without the use of a jury.
Since January 2011, under the Fines Act 2010, summary convictions fall into 5 categories of maximum fines. For instance, if someone is found liable for a class C fine on summary conviction, the maximum fine is €2,500. Additionally, the court has the option to impose a term of imprisonment instead of or in addition to a fine.
It is obligatory to calculate your tax obligations annually. Ensuring precise and current details on each transaction is essential for accurately determining the appropriate amount of tax you owe.
The records should include:
Keeping these records can save numerous administrative hours for PAYE and tax calculations. Failure to comply with these record-keeping requirements can lead to penalties for the business.
The tipping law in Ireland can have notable cost savings for businesses if payment transactions are tracked and split appropriately.
Businesses can avoid overcharging themselves on VAT when processing bills, particularly when a customer pays with a credit or debit card and the service charge or tip transaction is not separately recorded.
Calculations:
Outcomes:
Calculations:
Outcomes:
Failure to accurately track card and cash transactions may lead to an overestimation of tips allocated to staff members.
Because the legislation mandates businesses to distribute tips and service charges to their staff, errors in calculations may occur if they are not accurately tracked and instead estimated. By having every transaction accounted for there is greater clarity and transparency as to what is due to both the employees, the business and any costs associated which may be deducted.
Tipping laws in Ireland influence how businesses manage their staff, directly impacting employee satisfaction and staff turnover rates.
In Ireland, the new tipping law and increased transparency could boost employee satisfaction by relieving them of concerns about their owed tips. Directly assigned tips can enhance service staff motivation by showing a clear link between their efforts and rewards.
High staff turnover can be costly for businesses, necessitating ongoing recruitment and training. When tips are distributed fairly and transparently, it can lead to reduced turnover rates. Employees may be more likely to stay with an employer where there is an equitable tipping system that supplements their income reliably.
| Factors Influencing Staff Turnover | Impact |
| Perceived fairness of tips distribution | Positive correlation with lower turnover |
| Tip contribution to overall salary | Important factor in job retention decisions |
| Transparency in handling tips | Improves trust and reduces staff departure intentions |

In Ireland, how tipping is handled greatly influences how customers perceive their dining experience. Diners typically view their tipping discretion as a reflection of the service quality, a deeply rooted aspect of Ireland’s dining culture. Consequently, service quality directly impacts staff earnings, shaping customer expectations for their dining experience.
Customers generally perceive tipping as a direct form of feedback, and this can lead to expectations of high standards of service. In situations where service charges are added to bills, there is an expectation that this information is transparently communicated. When customers know that the service charge is distributed among the staff, it could reduce the necessity for additional tipping, thereby influencing their expectations regarding the customer-service dynamic.
A notable point is that international tourists may come with varying expectations based on their own country’s tipping practices. This variation can sometimes lead to misunderstandings.
Basically, the tipping law and its effects on businesses also influence customer expectations, which in turn, significantly contribute to shaping the overall customer experience in the Irish hospitality sector.
With technology continuously shaping consumer behaviour, Ireland might witness a transition towards digital tipping solutions. Mobile payment platforms like URocked solutions could incorporate smoother tipping features, prompting customers to electronically reward service.
The hospitality industry is expected to become more transparent about tipping, with businesses possibly revealing how tips are divided among staff. This shift may be motivated by businesses striving for compliance and accurate payment transactions, employees advocating for transparency, and consumer demand for ethical treatment of workers.
Changing social norms could result in expectations of tipping for a wider range of services, not just food and beverage. Businesses might need to adapt their practices and educate their teams about these evolving trends.
Digital advancements could introduce automated tipping suggestions on electronic Point of Sale (POS) systems, impacting consumer tipping behaviour and altering businesses’ dependence on gratuities to ensure fair compensation for staff.
Businesses may prioritise investing in staff training to boost customer satisfaction and improve the chances of receiving tips. This could be seen as crucial for their financial well-being, particularly for those operating in the service sector.

In Ireland, tipping is not legally mandated, but businesses often navigate the customary practice of tipping in a way that aligns with local expectations and enhances staff morale. Employers should be aware of several key considerations:
| Aspect | Suggestion |
| Tipping Policy | Ensure the establishment’s position on tipping is prominently displayed for clear understanding. |
| Service Charges | Justify any service charges and designate whether they are optional. |
| Transparency | Clearly explain how tips are handled to staff and customers alike. |
Following these guidelines can contribute to a positive working environment, customer satisfaction, and compliance with local customs, while steering clear of potential legal or financial pitfalls in Ireland’s hospitality sector.
In conclusion, navigating tipping laws is crucial for businesses in Ireland, as they significantly impact employee income, turnover rates, and operational costs. Legal compliance ensures transparency and motivates staff to enhance customer service, ultimately benefiting the business. By understanding these laws and implementing transparent tipping policies, businesses can foster a positive working environment while avoiding legal and financial pitfalls.